Metabolic Surgery
(DIABETES SURGERY) FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES
– Metabolic surgery is scientifically proven, very safe method for long term remission from type 2 diabetes.
– Mechanism of diabetes remission after metabolic surgery is different from other methods.
– Sleeve gastrectomy, Gastric bypass, and Sleeve plus bypass combination surgeries induce physiological changes leading to sufficient insulin production and reduced insulin resistance (increased insulin sensitivity) leading to long term control of blood sugars without the need for tablets or external insulin.
– These are performed on stomach and intestine by laparoscopic method (by putting small holes on the tummy).
– Metabolic and bariatric surgeries are essentially same. If the purpose of surgery is remission from type 2 diabetes and other co-morbid medical conditions, it is called metabolic surgery. If the purpose of surgery is weight loss, then it is called bariatric surgery.
– Individuals suffering from type 2 diabetes with excess weight benefit from metabolic surgery.
– Metabolic surgery helps individuals with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes regardless of their weight.
– Metabolic surgeries alter several factors, that control insulin production and insulin sensitivity.
– These alterations include increased Incretins (GLP 1, Peptide YY) and reduced Anti-incretins & Ghrelin.
– Incretins produced in ileum (The last part of the small intestine) increase insulin release in the presence of glucose.
– In metabolic surgeries, food reaches distal ileum (The end part of the small intestine) rapidly, resulting in increased GLP 1 production.
– GLP 1 increases size & number of insulin producing beta cells of pancreas. It also reduces insulin resistance.
– Anti-incretins are produced in duodenum (First part of the small intestine). They increase insulin resistance. In most bariatric/metabolic surgeries since duodenum is bypassed, anti-incretins are reduced.
– Ghrelin, produced in the stomach fundus, increases insulin resistance. As fundus of stomach is removed in most of metabolic surgeries, Ghrelin production is reduced.
– These physiological alterations result in increased Insulin production and increased Insulin sensitivity leading to long term diabetes remission.
– Metabolic surgery results in long term remission from type 2 diabetes.
– Blood sugars become normal even without using medications. And this control is long lasting.
– Metabolic surgeries help individuals with uncontrolled diabetes despite optimum medical treatment.
– Mr. Akiri Balaji used to suffer from obesity with 149 kg weight and uncontrolled type 2 diabetes with HbA1C of 11.7%. Dr. Amar performed ‘Sleeve gastrectomy with loop gastroileal bypass’ on him in Oct 2016. He lost 63 kg. His present weight is 86 kg and HbA1C of 3.9%. He is leading diabetes free life.
– Metabolic surgeries improve other medical problems like high blood pressure, high blood fats (hyperlipidemia), snoring (obstructive sleep apnea), joint pains (osteoarthritis) in significant number of individuals.
– These surgeries halt progression of obesity and diabetes induced complications and in certain percentage of patients, these problems also resolve.
– If your blood sugars are uncontrolled despite changing lifestyle, using tablets and insulin, then you need metabolic surgery to control blood sugars.
– If you have excess weight, you can undergo metabolic surgery for diabetes remission even if your blood sugars are under control.
– Several studies demonstrated superior results with metabolic surgery compared to medical management in patients suffering from type 2 diabetes and obesity.
– International Diabetes Organizations included metabolic surgery in the treatment algorithm of type 2 diabetes.
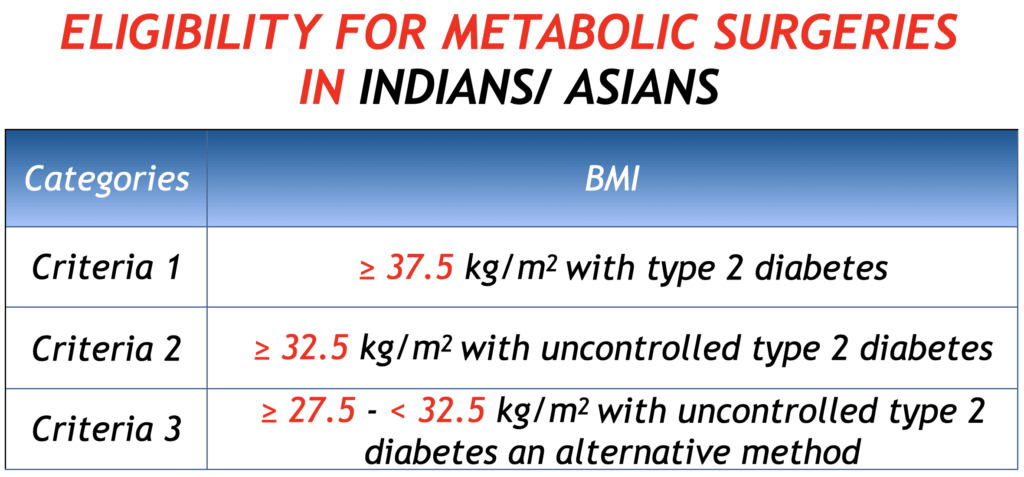
According to this algorithm, in Indians/ Asians, metabolic surgery is
- considered if BMI is ≥ 27.5 kg/m2 with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes
- recommended if BMI is ≥ 32.5 kg/m2 with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes
- recommended if BMI is ≥ 37.5 kg/m2 with mere presence of type 2 diabetes.
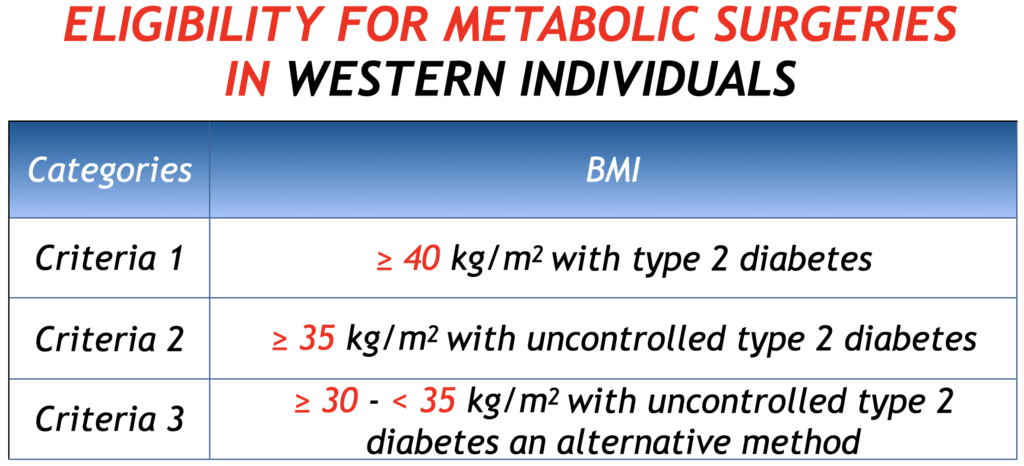
And in individuals from Western countries, metabolic surgery is
- considered if BMI is ≥ 30 kg/m2 with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes
- recommended if BMI is ≥ 35 kg/m2 with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes
- recommended if BMI is ≥ 40 kg/m2 with mere presence of type 2 diabetes.
– If your weight is normal or your BMI is < 27.5 kg/m2 and if you have uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes leading to health risks despite optimum medical treatment, then you can be considered for metabolic surgery to control diabetes, after discussing with your endocrinologist.
I have type 1 diabetes, will metabolic surgery help me?
– Metabolic surgery acts by enhancing insulin production and sensitivity.
– In type 1 diabetes, there is reduced or absent production of insulin, mostly due to autoimmune destruction of beta cells of pancreas (body defence senses its own cells as enemies and destroy them). – So metabolic surgery won’t help individuals with type 1 diabetes. It is contraindicated.
– The most popular metabolic surgeries are
- Sleeve gastrectomy (SG),
- Roux-en-y gastric bypass (RYGB) and
- Mini gastric bypass – One anastomosis gastric bypass (MGB – OAGB).
– But these popular surgeries have certain limitations.
– Diabetes remission is significantly more with diversion surgeries since physiological changes after diversion procedures are high.
– Bilio-pancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD DS) is the most effective metabolic surgery since physiological changes are very high, but malabsorption risk is also very high since most of the small intestine is bypassed.
– There are several modifications of BPD DS to reduce malabsorption without compromising on efficacy. BPD DS and its modifications are known as Sleeve plus procedures or Sleeve plus bypass combination procedures. These sleeve plus bypass combination surgeries achieve durable control of type 2 diabetes.
– These modifications include
- Sleeve with loop duodenal switch (SLDS), also known as Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass with sleeve (SADI S),
- Sleeve gastrectomy with loop gastroileal bypass (SG LGIB), also known as Single anastomosis sleeve ileal bypass (SASI Bypass)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with loop duodeno-jejunal bypass (SG LDJB).
- Sleeve gastrectomy with loop gastrojejunal bypass (SG LGJB), also known as Single anastomosis sleeve jejunal bypass (SASJ Bypass)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with proximal jejunal bypass (SG PJB)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with jejunoileal anastomosis (SG JIA)
- Sleevee gastrectomy with duodenojejunal bypass (SG DJB)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with transit bipartition (SG TB)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with duodenoileal interposition (SG DII), also known as Diverted sleeve gastrectomy with ileal interposition (DSG II)
- Sleeve gastrectomy with jejunoileal interposition (SG JII), also known as Sleeve gastrectomy with ileal interposition (SG II)
– Adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), Greater curve plication (GCP) were once popular, but got out dated because of poor results.
– There are few endoscopic procedures for diabetes control. These include
- Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG)
- Intragastric balloon (IGB)
- Swallowable gastric balloon (SGB)
– Intra gastric balloon (IGB), and Swallowable gastric balloon (SGB) are less effective compared to metabolic surgeries for diabetes remission because these endoscopic procedures act mainly be food restriction. Physiological changes after these procedures are negligible. Chances of diabetes recurrence are very high once balloon is removed. They may have a role in well motivated individuals with mild diabetes.
– Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is better intra gastric balloon or swallowable gastric balloon as there are some physiological changes after ESG, but these changes are less than those after metabolic surgeries. Chances of diabetes recurrence are high once stomach expands after ESG especially if life style modifications are not followed. ESG has a role in those individuals who have uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and in whom 10 to 20 kg weight loss helps to bring diabetes under control. It also can be considered in those who are afraid of metabolic surgeries.
– Metabolic surgeries are very safe and highly effective if they are performed on right candidate by qualified surgeons.
– Major complications like bleeding, leak, blood clots in legs are very rare (< 1%).
– Bleeding, leak from staple lines are very rare problems because of usage of high end staplers, guns and vessel sealers. Even if they occur, they can be rectified.
– To prevent blood clots in the legs, you will be prescribed anticoagulant medications.
– Hair loss can occur because of weight loss (When surgery is performed for diabetes with obesity) but this is temporary. Once weight is stabilized all the lost hair will come back.
– Skin loosening can occur because of weight loss (When surgery is performed for diabetes with obesity) but this is temporary. Weight loss is fast and skin tightening is slow. So you may look weak and skin looks wrinkled during weight loss period. Once weight loss stops and weight is stabilised, skin becomes tight and match weight loss in majority of individuals.
– Because of weight loss (When surgery is performed for diabetes with obesity), people can develop gall bladder stones. Urspdeoxycholic Acid tablets for 1 to 1.5 years are needed to prevent formation of stones in gall bladder during weight loss period.
– To prevent vitamin, mineral and protein deficiencies, you will be prescribed post bariatric multivitamin, mineral and protein supplements.
– You will have food aversions, which will settle over a period of time.
– Individuals eligible for metabolic and bariatric surgeries are fully evaluated by a dedicated team comprising of expert metabolic & bariatric surgeon, dietician, endocrinologist, physician, cardiologist, pulmonologist, sleep apnea specialist, psychiatrist and psychologist. This is to perform surgery at maximum safety and minimize risks near to zero.
– Patients are counselled well about various surgeries, pre & post operative requirements.
– Operation suites for these surgeries are designed at international standards, equipped with high end technology including full HD laparoscopic systems, advanced vessel sealing devices to perform complex bariatric and metabolic surgeries.
– Advanced surgical ICU facilities and 24 hr intensive care specialists coverage ensures maximum safety.
– Dr. Amar performed ‘Sleeve gastrectomy’ surgery on his father Dr. V. Brahma Reddy in Jan 2014. He lost 34 kg, and leading a diabetes free life. His HbA1C reduced from 9.2% to 5.7%.
– Dr. Amar also performed ‘Sleeve gastrectomy with duodenoileal interposition’ surgery on his brother-in-law Mr. Srinivasa Reddy in Mar 2013 for uncontrolled diabetes. He lost 23 kg and his sugars are under control even without medications. His HbA1C reduced from 9.6% to 5%.
– He also performed ‘Sleeve gastrectomy with loop gastroileal bypass’ surgery on his mother-in-law Mrs. Vijaya Lakshmi in Aug 2016 for obesity and diabetes. She lost 31 kg and leading healthy active life without diabetes. Her HbA1C reduced from 7% to 4.4%.
– Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and gastric bypass (RYGB, MGB – OAGB) are most commonly performed obesity surgeries worldwide.
– In most individuals, diabetes remission is durable after SG, RYGB and MGB – OAGB surgeries.
– But diabetes recur in some individuals, even after properly performed surgery. This is due to body adaptation to the physiological changes or not sticking to lifestyle modifications.
– When diabetes recur after meetabolic surgery, first they will be advised to change their life style. Some require adjuvant therapy in the form of adding medications
– If lifestyle modifications and medications fail, then these individuals need revision surgery in the form of adding ‘ileal diversion’. This is necessary to restore significant physiological changes needed to induce diabetes remission again.
– Examples include
- Duodenal switch (DS), ’
- Loop duodenal switch (LDS) or Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass’ (SADI)
and
- Loop gastroileal bypass (LGIB).
– Individuals with inadequate diabetes control after first surgery, also benefit with revision surgery.
– Metabolic and bariatric surgeries can be performed safely even in unmarried females and married females planning for pregnancy in future.
– These surgeries improve fertility.
– Only precaution needs to be taken is pregnancy should not be planned in first 18 months after surgery.
– Diabetes can lead to infertility. Metabolic surgery improves fertility.
– Metabolic and bariatric surgeries are performed in individuals between 18 and 65 years age.
– Surgeries can be considered in those below 18 years, if all other methods failed to induce weight loss.
– Surgeries can also be considered in selected individuals above 65 years, if their general condition allow them to undergo surgery.